Ross Sea Ice Shelf
The Ross Sea Ice Shelf melts from the land outward towards the sea seasonally, creating an area of open water between the ice shelf and land. This area of open water is called a polynya. The Ross Sea polyna is a Latent Heat Polynya because it is formed by ocean currents and wind.
The Ross Sea Ice Shelf and polynya is important for the research being done in Antarctica this winter. Scientists are going to be doing research in and around the polynya to find out more about what is going on in the area. In order for the scientists to deploy their research equipment in the water the polynya needs to be large so watching the polynya open up and the ice move out towards the sea is very important.
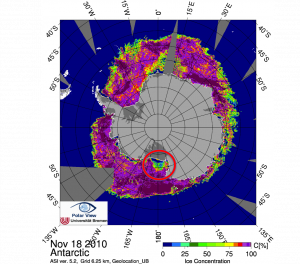
Above is an image showing the current ice concentrations in Antarctica. The area circled is the Ross Sea Ice Polynya. (Source: University of Bremen)
Check out the Daily Updated AMSR-E Sea Ice Concentration Images for real-time images.
The images below from Polar View are satellite images of the West Ross Sea Ice Shelf. The first image is from the beginning of September and the second image is from the end of October. As seen in the images the Ice Shelf is breaking up as we get closer to the Antarctic summer.

The above image is from September 2010 and shows the Ross Sea Ice Shelf in white and theAntarctic continent in black.

This satellite image from the end of October shows the Ross Sea Ice Shelf beginning to break up. In this image the ocean is black, and the ice on the shelf and Antarctic continent is grey.
This post was compiled by undergraduates Shannon, Bill and John as part of their Antarctic Research class.


 November 24, 2010
November 24, 2010 







Comments are closed.